Cardiovascular System
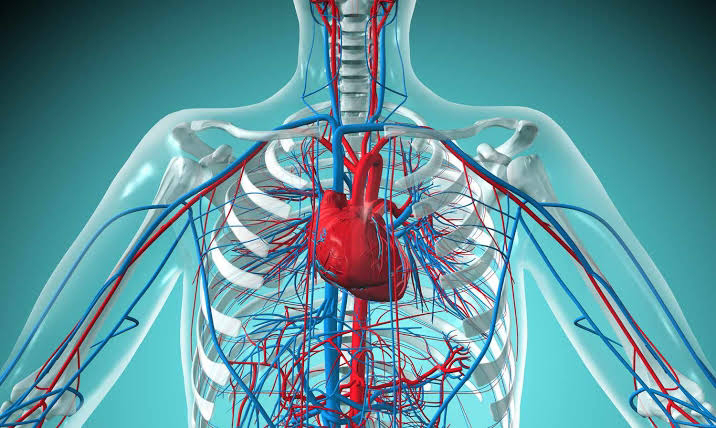
In all multicellular organisms, living cells require nourishment, oxygen, and other important chemicals. Furthermore, waste or dangerous chemicals must be eliminated on a constant basis to ensure that tissues work properly. It is consequently necessary to have efficient pathways for transporting these chemicals to and from the cells. The cardiovascular system transports gasses, nutrition, hormones, and cellular waste throughout the body. It comprises mostly of three interconnected components: blood, the heart, and blood vessels. Blood Blood is a connective tissue made up of blood plasma and other components. Blood is somewhat alkaline, with pH ranging from 7.3 to 7.4. It makes up 20-30% of extracellular fluid, accounting for 8% of total body mass. Blood serves the following vital functions: Transportation of gases like oxygen and carbon oxide, nutrients, hormones, heat and wastes. Regulation of pH, body temperature, and water content of cells Protection ag...

